The Ancestor Hunt regularly adds and updates new collection links, as well as searches for and fixes broken links.
(This page's most recent update is December 2025)
Want to improve your newspaper research skills? Use the resources of the Newspaper Research Academy at Academy
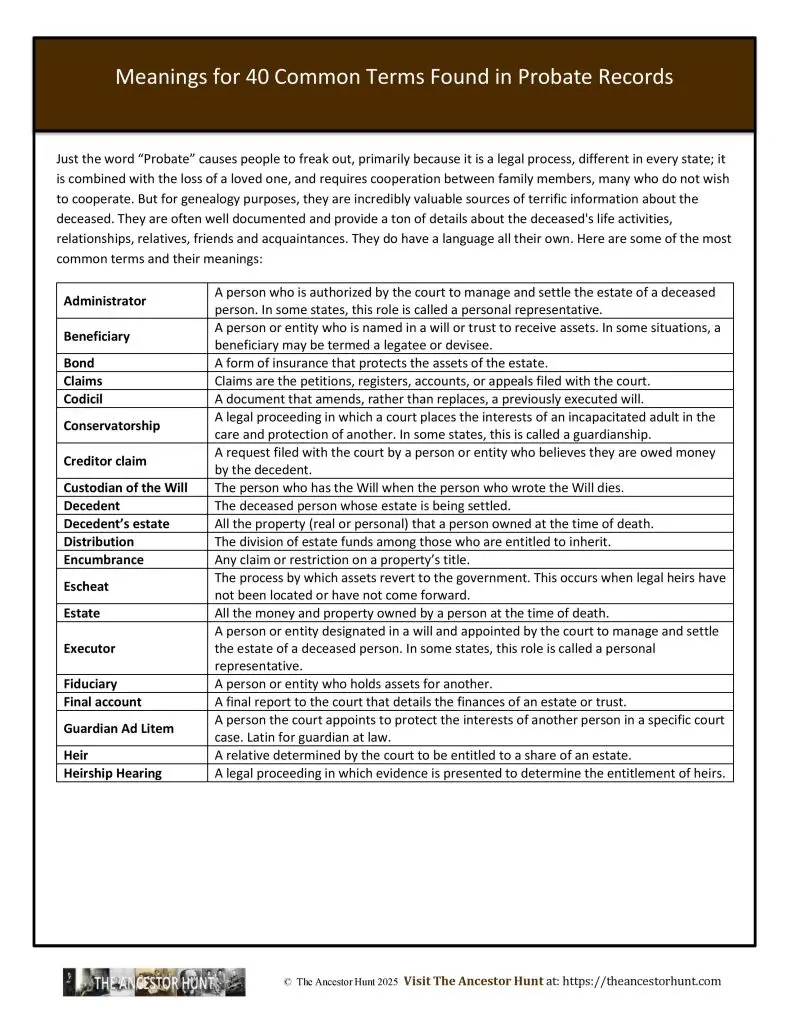
Just the word “Probate” causes people to freak out, primarily because it is a legal process, different in every state; it is combined with the loss of a loved one and requires cooperation between family members, many of whom do not wish to cooperate. But for genealogy purposes, they are incredibly valuable sources of terrific information about the deceased. They are often well-documented and provide a ton of details about the deceased’s life activities, relationships, relatives, friends, and acquaintances. They do have a language all their own.
Download the Quicksheet PDF
To download the Quick Sheet PDF, click on the Download button below:
For all the previously published Quick Reference Guides, click on QuickSheets.
Genealogy QuickSheets – Frequently Asked Questions
- 100 Best Free Online Genealogy Websites
- Beyond the Search Engine: Using Google Databases for Genealogy Research
- 64 Genealogy Items to Collect from Your Home
- United States Genealogical and Historical Societies
- 24 Places Where You Can Find Your Ancestors Occupation
- 13 Types of Genealogical Information You Can Find in Old Yearbooks
- 16 Places Where You Can Find Genealogy and Family History Books
- Easy Cousin Relationship Chart